Queen Victoria I of England, born Alexandrina Victoria on May 24, 1819, reigned from June 20, 1837, until her death on January 22, 1901. She ascended to the throne at the age of 18, following the death of her uncle, King William IV.
Victoria’s reign, known as the Victorian era, was one of Britain’s significant social, economic, and technological changes. She married her cousin, Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, in 1840, and their marriage was a cornerstone of her reign, with Albert playing a key role in her governance and reforms. Queen Victoria’s reign witnessed the expansion of the British Empire, the Industrial Revolution, and significant advancements in science and technology.
She became a symbol of stability and continuity during a period of rapid change, and her reign profoundly impacted British society and politics. Victoria’s reign also saw the rise of constitutional monarchy, as the monarchy’s powers became increasingly limited by Parliament. Victoria’s long reign and strong influence earned her the title of “the Grandmother of Europe” due to her numerous descendants who married into royal families across the continent.
Early Life

Queen Victoria, born Alexandrina Victoria on May 24, 1819, was the only child of Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn, and Princess Victoria of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld. Her father died when she was just eight months old, leaving her to be raised by her mother, who exerted a significant influence on her upbringing.
Victoria’s early life was marked by seclusion and strict supervision by her mother and her mother’s adviser, Sir John Conroy. This upbringing, known as the “Kensington System,” aimed to control Victoria’s access to others and thereby influence her future reign. Despite this, Victoria received a comprehensive education in history, literature, languages, and politics.
As a child, Victoria was aware of her position in the line of succession but had limited contact with the royal court. Her closest companions were her half-sister, Princess Feodora of Leiningen, and her governess, Baroness Louise Lehzen, who played a significant role in her education and upbringing.
Victoria’s life changed dramatically in 1837 when her uncle, King William IV, died, and she ascended to the throne at 18. This marked the beginning of her long and influential reign as Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom.
Ascension To The Throne

Queen Victoria’s ascension to the throne was a significant moment in British history. On June 20, 1837, at the age of 18, Victoria became queen following the death of her uncle, King William IV. Her ascension occurred after a period of political uncertainty and transition.
Victoria’s uncle, King William IV, had no legitimate children, so the throne passed to his niece, Victoria, as the next in line of succession. Victoria’s father, the Duke of Kent, had been the fourth son of King George III, making her the king’s granddaughter.
Her accession to the throne was met with both excitement and apprehension. As a young, inexperienced queen, there were concerns about her ability to rule effectively. However, Victoria quickly proved herself to be a capable and determined monarch, asserting her authority and taking an active role in governance.
Her coronation occurred on June 28, 1838, at Westminster Abbey, where she was crowned queen in a lavish ceremony. Despite initial doubts, Victoria’s reign would go on to become one of the longest and most prosperous in British history, shaping the course of the 19th century and leaving a lasting legacy on the British Empire.
Marriage And Family Life

Queen Victoria’s marriage and family life were central to her reign and personal happiness. She married her first cousin, Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, on February 10, 1840, in what became one of history’s most famous royal unions.
Victoria and Albert’s marriage was not merely a political arrangement but a genuine love match. They shared a deep affection and mutual respect for each other. Albert became Victoria’s trusted advisor and confidant, playing a significant role in her governance and decision-making.
The couple had nine children together, who married into royal families across Europe, earning Queen Victoria the title “the Grandmother of Europe.” Their children included Victoria, Princess Royal, who married the German Emperor Frederick III; Edward VII, who succeeded Victoria as king; Princess Alice, who married Louis IV, Grand Duke of Hesse; Alfred, Duke of Edinburgh and of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha; Helena, Princess Christian of Schleswig-Holstein; Princess Louise, Duchess of Argyll; Prince Arthur, Duke of Connaught and Strathearn; Prince Leopold, Duke of Albany; and Princess Beatrice, who married Prince Henry of Battenberg.
Despite their happy family life, Queen Victoria’s marriage to Prince Albert was not without its challenges. Albert faced criticism for his influence over Victoria and the royal household, and their relationship was tested by personal tragedies, including Albert’s premature death at the age of 42 in 1861. Victoria was devastated by Albert’s death and entered a prolonged period of mourning, wearing black for the rest of her life and withdrawing from public life to a certain extent.
Nevertheless, Queen Victoria’s marriage and family life were a source of strength and stability throughout her reign, and her descendants continue to play significant roles in European royalty to this day.
Political Influence And Reforms
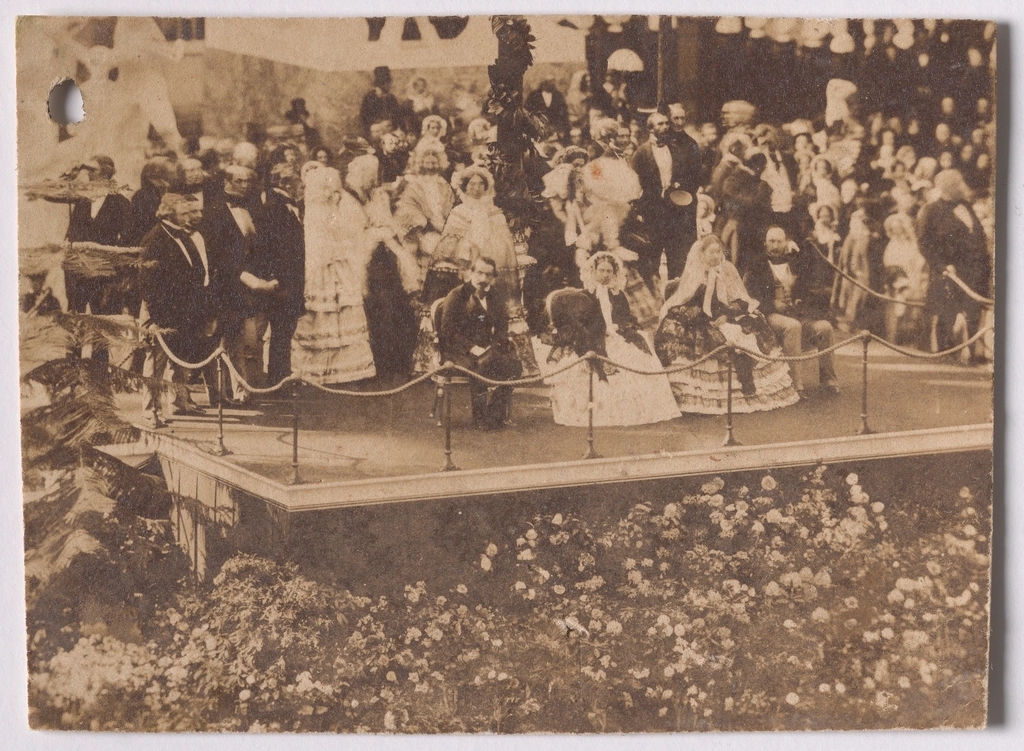
Queen Victoria’s political influence and reforms were notable aspects of her reign, despite the constitutional limitations on her powers as a constitutional monarch. While she did not have the authority to make laws or govern directly, Victoria played a significant role in shaping public opinion and influencing political decisions through her relationships with prime ministers and her public statements.
One of Victoria’s key political influences was her partnership with her husband, Prince Albert. Albert, who was well-educated and forward-thinking, profoundly impacted Victoria’s views and decisions. Together, they championed various social and political causes, including education, public health, and the welfare of the working class.
During Victoria’s reign, there were significant social and economic changes, including the Industrial Revolution and the growth of urbanization. Victoria supported reforms aimed at improving the lives of ordinary people, such as the Factory Acts, which regulated working conditions in factories, and the Public Health Act, which aimed to improve sanitation and public health standards in cities.
Victoria also played a role in foreign affairs, particularly in matters relating to the British Empire. She was a strong supporter of imperial expansion and played a symbolic role in the growth of the Empire, earning her the title “Empress of India” in 1876.
While Victoria’s political influence was often behind the scenes, her reign was characterized by stability and continuity, which helped to maintain public confidence in the monarchy during a period of significant change. Her reign also saw the gradual evolution of constitutional monarchy, with power increasingly shifting towards elected representatives in Parliament.
Overall, Queen Victoria’s political influence and reforms helped to shape the course of British history and left a lasting legacy on the nation and the wider British Empire.
Cultural Impact And Legacy
Queen Victoria’s cultural impact and legacy are profound, leaving an indelible mark on British society and beyond. Here are some key aspects of her cultural impact and legacy:
Victorian Era: Queen Victoria’s reign, which lasted from 1837 to 1901, is known as the Victorian era. This period saw significant social, economic, and technological changes, including the Industrial Revolution, urbanization, and the expansion of the British Empire. The Victorian era is characterized by its strict social norms, moral values, and emphasis on propriety and respectability.
Influence on Fashion and Style: Queen Victoria’s personal style and preferences influenced fashion trends during her reign. Her fondness for wearing black following the death of her husband, Prince Albert, set a mourning fashion trend that lasted for decades. The Victorian fashion aesthetic, characterized by elaborate dresses, corsets, and formal attire, is still iconic today.
Imperialism and the British Empire: Queen Victoria presided over the expansion of the British Empire, which became the largest Empire in history during her reign. Her reign saw British dominance in global politics, trade, and culture, shaping the modern world and leaving a lasting legacy on former colonies and territories.
Literature and Arts: The Victorian era was a golden age for literature and the arts. Writers such as Charles Dickens, the Brontë sisters, and Oscar Wilde flourished during this period, producing timeless literary works that continue to be celebrated today. Victorian art and architecture also reflect the values and aspirations of the era, with majestic buildings and romantic landscapes.
Public Monarchy and Royal Influence: Queen Victoria’s reign marked the beginning of the modern public monarchy, with the royal family becoming more accessible to the public through events such as royal weddings, births, and public appearances. Victoria’s strong sense of duty and moral values helped shape the public perception of the monarchy and reinforce its role as a national identity and continuity symbol.
Family Legacy: Queen Victoria and Prince Albert’s nine children married into royal families across Europe, earning Victoria the title “the Grandmother of Europe.” Their descendants include numerous European monarchs and influential figures, shaping the course of European history and politics.
Overall, Queen Victoria’s cultural impact and legacy are far-reaching, influencing not only British society but also global politics, culture, and the arts for generations to come.






Leave a comment